If you have ever stumbled upon a decade-old computer, you might have seen how the BIOS looks.
There are comparatively fewer options to use and you are not able to use multiple peripherals in the BIOS.
However, the BIOS you see today is rich in the interface that can support a lot of input devices and allows you to boot securely into your operating system.
These two BIOS are known as Legacy and UEFI. You might get confused between the two as you may see “BIOS” written with both of them but they are not the same.
Their job is definitely similar but there are a good number of differences you should know.
What Is Legacy BIOS?
Legacy mode is basically a boot process by the BIOS firmware that initializes and establishes the connection between your computer hardware and input devices.
Legacy BIOS was previously called just “BIOS” which translates to Basic Input/Output System. It is a firmware that is inbuilt on a motherboard and when the POST process starts, the BIOS looks for the MBR or Master Boot Record on the storage drives.
When MBR locates the boot loader, the BIOS successfully loads your operating system kernel.
What Is UEFI?
UEFI or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface is a mini operating system that runs on top of a computer firmware. It connects a computer’s firmware to the operating system at the boot.
UEFI mode in modern computers replaces the Legacy BIOS which was a lot slower and less secure. Its location is different from the Legacy BIOS but has basically the same job of loading your operating system. The difference between them is how they work.
Don’t get confused between BIOS and UEFI as both are different where UEFI replaces the former. Modern computers still come with “BIOS” labeling instead of UEFI to avoid confusing the users, however, their process of booting is a little different.
UEFI vs Legacy BIOS
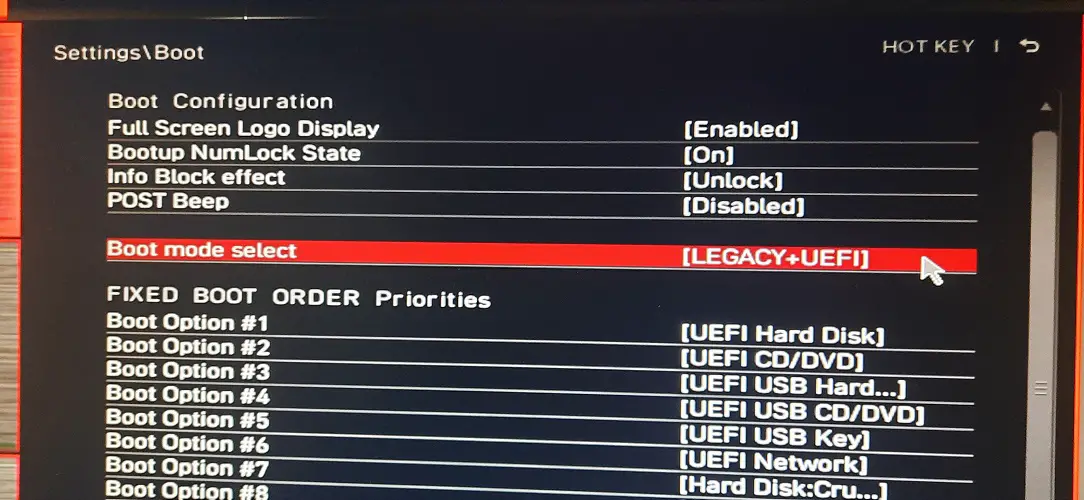
Older motherboards that had Legacy BIOS couldn’t support multiple peripherals at the startup because of their low executable space which was only 1024KB.
While the Legacy BIOS runs in a 16-bit mode, the UEFI runs either in a 32-bit or 64-bit mode. This gives users the option to use both the mouse and keyboard in UEFI instead of just the keyboard in Legacy BIOS. Moreover, the support extends to USB, ThunderBolt, and eSATA devices.
The interface and the options you could have in the Legacy BIOS were limited and it was super slow in booting the system. This would generally take up to or more than 30 seconds.
UEFI on the other hand provides support to multiple devices at the start and has a much better interface.
It also has much better security, better efficiency, and can support bigger capacity storage drives(talk about millions of Terabytes).
Basically, UEFI is a replacement for the Legacy BIOS to speed up the boot process and supports more storage drives.
It can support up to 9 Zettabytes of storage drive size compared to only 2.2 Terabytes by Legacy BIOS. So, if you have multiple storage drives installed with more than 2.2 TB of storage space, this means your motherboard supports the UEFI mode.
However, if you are unsure, you can read our post on how to check if your motherboard supports UEFI or not.
That said, one of the most important features of UEFI is the secure boot that prevents the loading of unauthorized or unsigned applications at the start.
Where Is UEFI Stored?
While Legacy BIOS is stored on an EPROM or Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory chip on a motherboard, UEFI is stored on ESP or Extensible Firmware Interface System Partition.It is located on the storage drive, unlike the BIOS which resides on the firmware. UEFI file has a “.efi” extension whereas the Legacy BIOS has “.exe”.
Legacy BIOS uses the MBR for determining the location of the operating system and stores a table with details of the partitions on the storage drive.
On the other hand, UEFI uses GPT or GUID Partition Table to store the details of partition tables. With GPT, it is possible to create multiple partitions because UEFI can support significantly higher storage space.
Final Words
This was a brief introduction to both UEFI and Legacy BIOS and how they work. While older motherboards use to come with Legacy BIOS mode, some modern motherboards come with both Legacy and UEFI modes to choose from.
Let us know if you have any questions about either or both of them in the comments below.
Related: