Computer hardware is evolving for decades and one thing that helps to run everything properly is the motherboard. It connects every peripheral and component for a fully functional computer and the history of computers has seen many types of motherboards in the course.
There are 4 most popular types of motherboards used in computers today. They are as follows:-
- Mini-ITX
- Micro-ATX
- ATX
- E-ATX
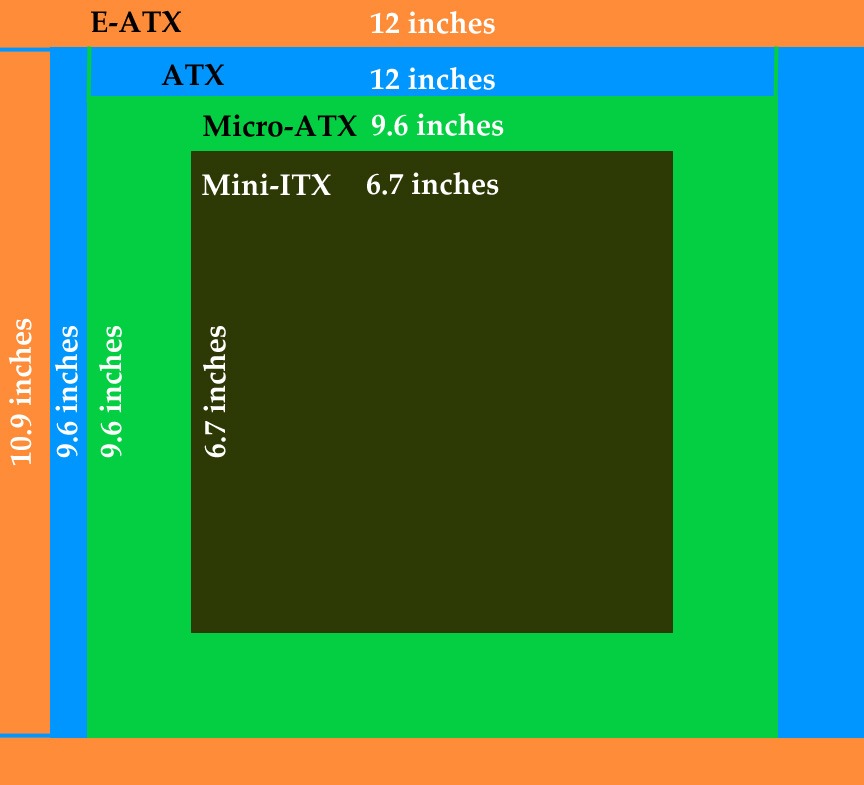
These are the common terms that represent their form factors. Form factors represent the sizes of the motherboards and their features. The smaller the board is, the lesser the features are. This is a common thing but there are exceptions where you can find more features on a smaller board than on a bigger one.
Motherboard Size Comparison
Let me explain how each one of these looks and what features they generally have.
Related: What are Motherboard Standoffs?
Mini-ITX motherboard
From the name itself, you can tell that the size of the Mini-ITX motherboard will be smaller than the other ones. Generally, it’s the smallest form factor for day to day purposes. Take a look at how a modern Mini-ITX motherboard looks:-
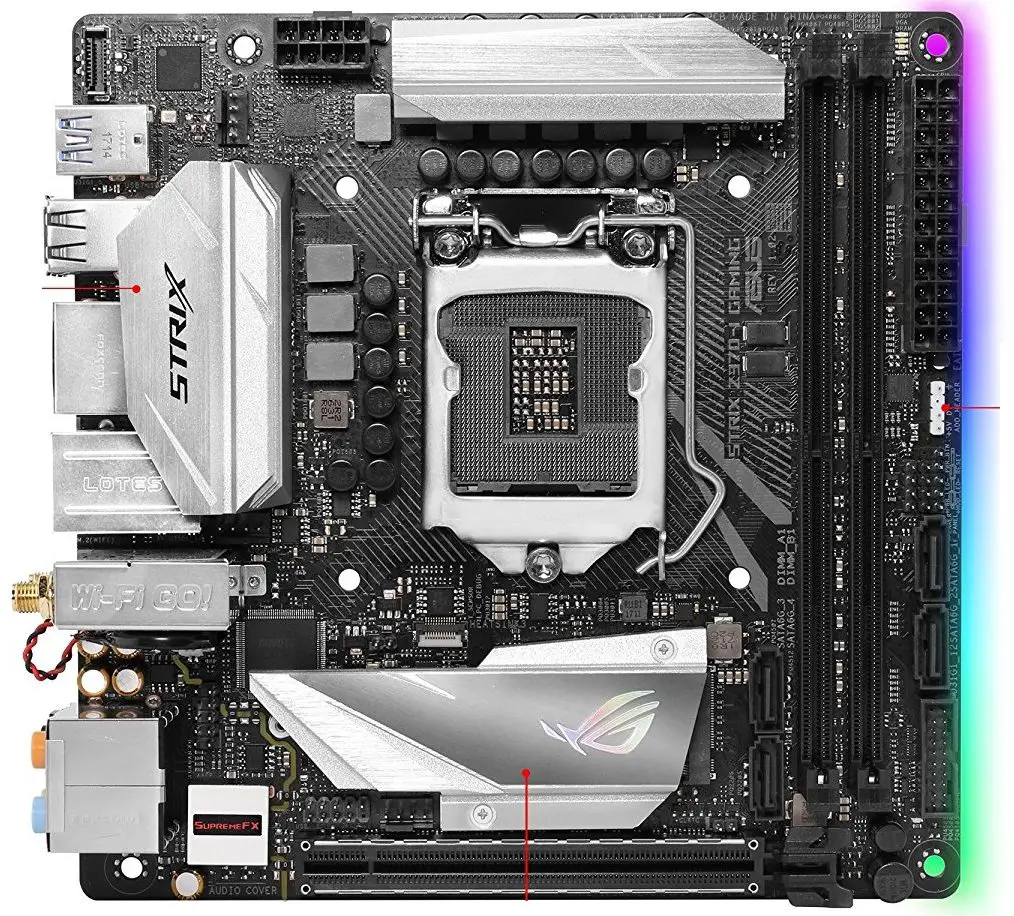

This is a very small motherboard that has limited features but not necessarily the minimum. A Mini-ITX motherboard measures around 17x 17 CM or 6.7 x 6.7 inches in dimensions.
Uses of Mini-ITX motherboards
A Mini-ITX motherboard provides all the basic features that a bigger board can provide but in a compact area. Some people prefer building a PC in a Mini-ITX case which is also much smaller than an ATX case and provides a compact solution to those who don’t have enough space for their PCs.
Features
A modern Mini-ITX motherboard comes with fewer ports and slots. There will be never more than 1x PCI-Ex 16 Slot on a Mini-ITX motherboard and never more than 2x DIMM Slots for memory. Almost every ITX board has only 4x SATA ports for storage and a few Fan headers. But features like Overclocking may vary. Basic budget ITX motherboards don’t have unlocked chipsets but expensive ones may have unlocked chipsets for overclocking the processors.
Understanding these features are important to differentiate between the types of motherboards and it should be noted that with each other passing, the features may change or get upgraded.
Micro-ATX motherboard
A Micro-ATX motherboard is bigger than the ITX motherboard and smaller than an ATX motherboard. Generally, it has dimensions as 24.4 x 24.4 CM or 9.6 x 9.6 Inches. But some motherboards may have dimensions as 9.6 x 8.1 inches or 24.4 x 20.6 CM depending upon the slots and ports they come with. A modern mid-high end Micro-ATX motherboard looks like the following:-
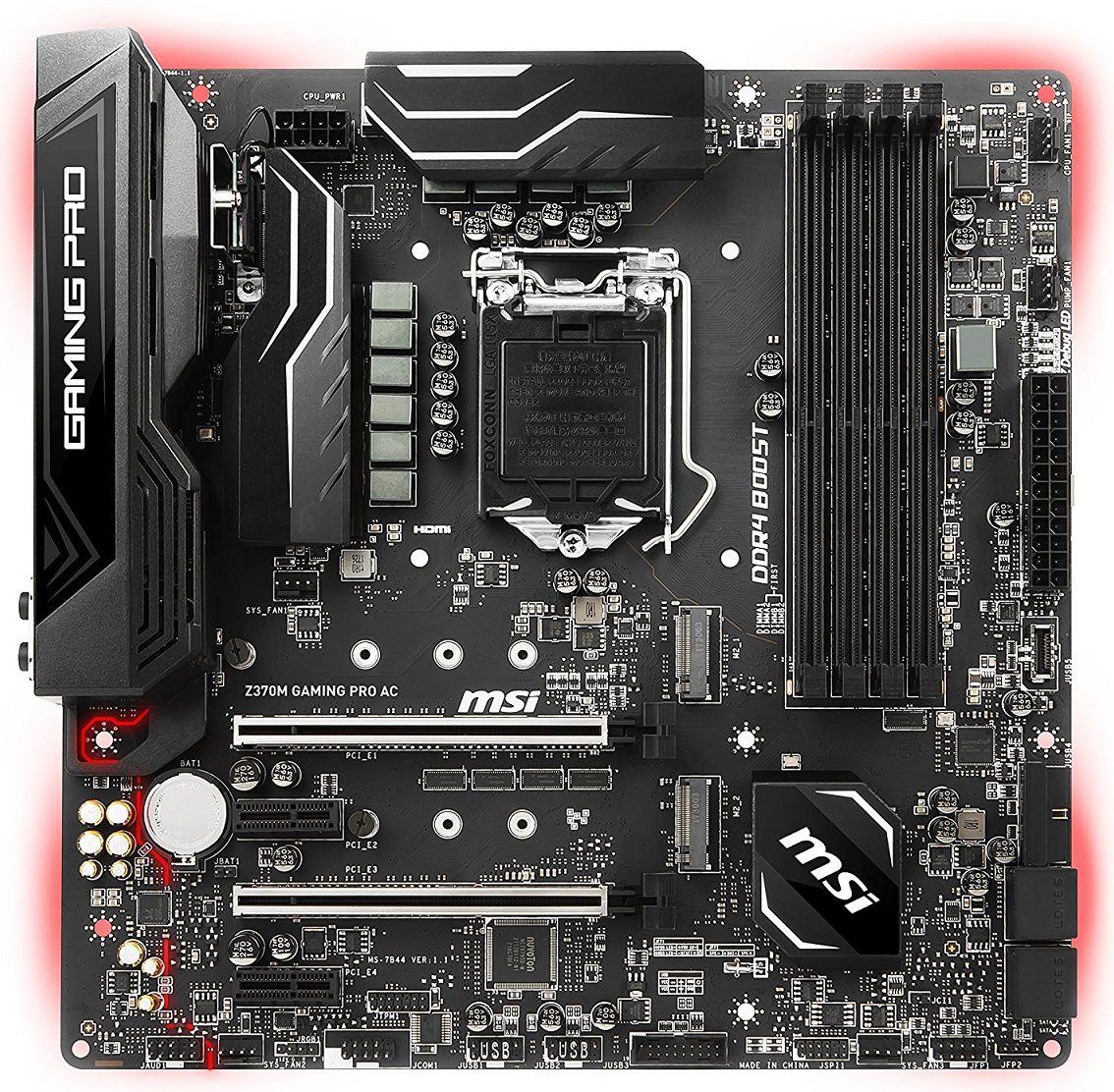
Uses of M-ATX motherboards
A Micro-ATX motherboard serves both the purpose of good features and compactness. As it is bigger than an ITX motherboard, it sports more slots and ports while remaining smaller than a Full ATX motherboard. The size also varies making it a flexible form factor.
Features
Depending upon the dimensions the number of PCI slots and Memory slots differs in quantity. A Micro-ATX board can either have 2x DIMM slots OR 4x DIMM slots which makes it wider or narrower. Similarly, a particular Micro-ATX board can have only 1x PCI-Ex 16 slot but the other one can have up to 3x PCI-Ex 16 slots. These boards come in a variety of features ranging from budget to high-end having a great VRM section, big heatsinks, more fan headers and more storage facilities.
ATX Motherboard
The standard ATX form factor is the most popular among all the types of motherboards because it has every feature which can fulfil almost every requirement, be it for gaming or productivity. An ATX motherboard is larger than a Micro-ATX and smaller than an E-ATX motherboard. A modern ATX motherboard looks as follows:-
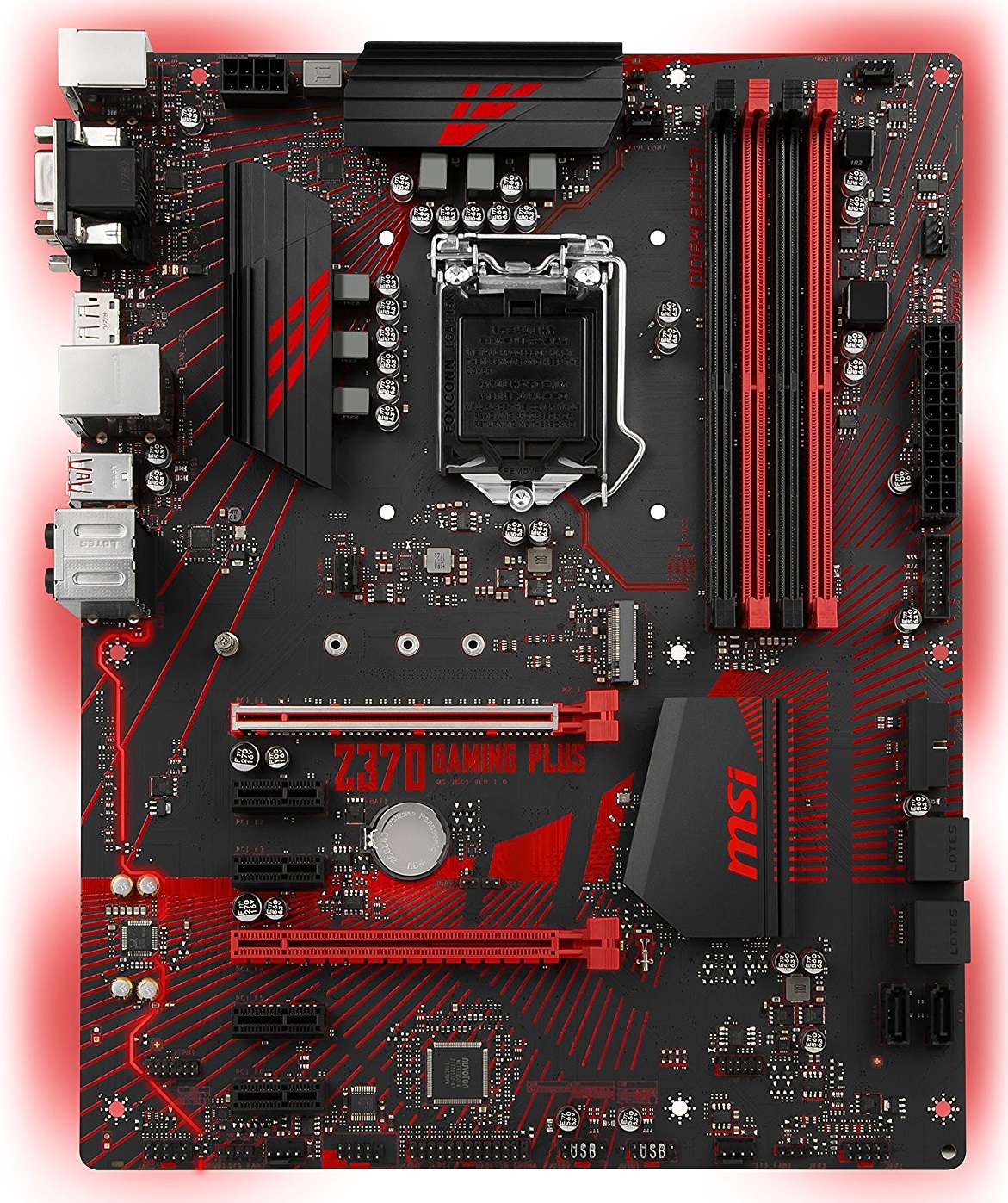
An ATX motherboard packs in tons of features with a lot of upgradability that is enough for several years depending on the user’s needs. More ports and slots are available as compared to Mini-ITX and Micro-ATX but it costs more than the two form factors mentioned above. The general dimensions of an ATX motherboard are 12 x 9.6 inches or 30.5 x 24.4 CM. Almost every Mid-Tower can fit in an ATX motherboard without any problem.
Uses of ATX motherboards
An ATX motherboard provides almost every feature that an enthusiast may need including overclocking, storage, high-end CPUs, memory, and cooling. An ATX form factor motherboard is a type of motherboard that is good for those who don’t have any space problems and have a good-sized CPU cabinet that takes more space than a Micro-ATX or Mini-ITX case. Also, ATX motherboards look better in design and fill up the interior of a chassis.
Features
One of the best advantages of an ATX motherboard is that it provides several PCI slots and at least 4x DIMM slots that can support a lot of memory. Modern motherboards support more than 32GB of RAM easily. These motherboards may or may not have an unlocked chipset but those having unlocked chipsets have very good VRMs with efficient heatsinks for stable overclocking.
These motherboards, in general, have a lot of fan headers for connecting the chassis fans, radiators as well as custom liquid coolers. Also, these have a lot of SATA ports and other storage device ports which increases the overall capability of an ATX motherboard to connect more storage devices. Not only that, high-end ATX motherboards have 3-4 PCI-Ex 16 slots that are capable of handling multiple graphics cards.
E-ATX motherboard
An E-ATX motherboard is something not very common among PC builders. Many PC builders and even enthusiasts prefer to stay with an ATX motherboard compared to EATX as well as the other types of motherboards. EATX motherboards come with the most features and powerful solutions for every operation. Following is an example of a modern E-ATX motherboard:-
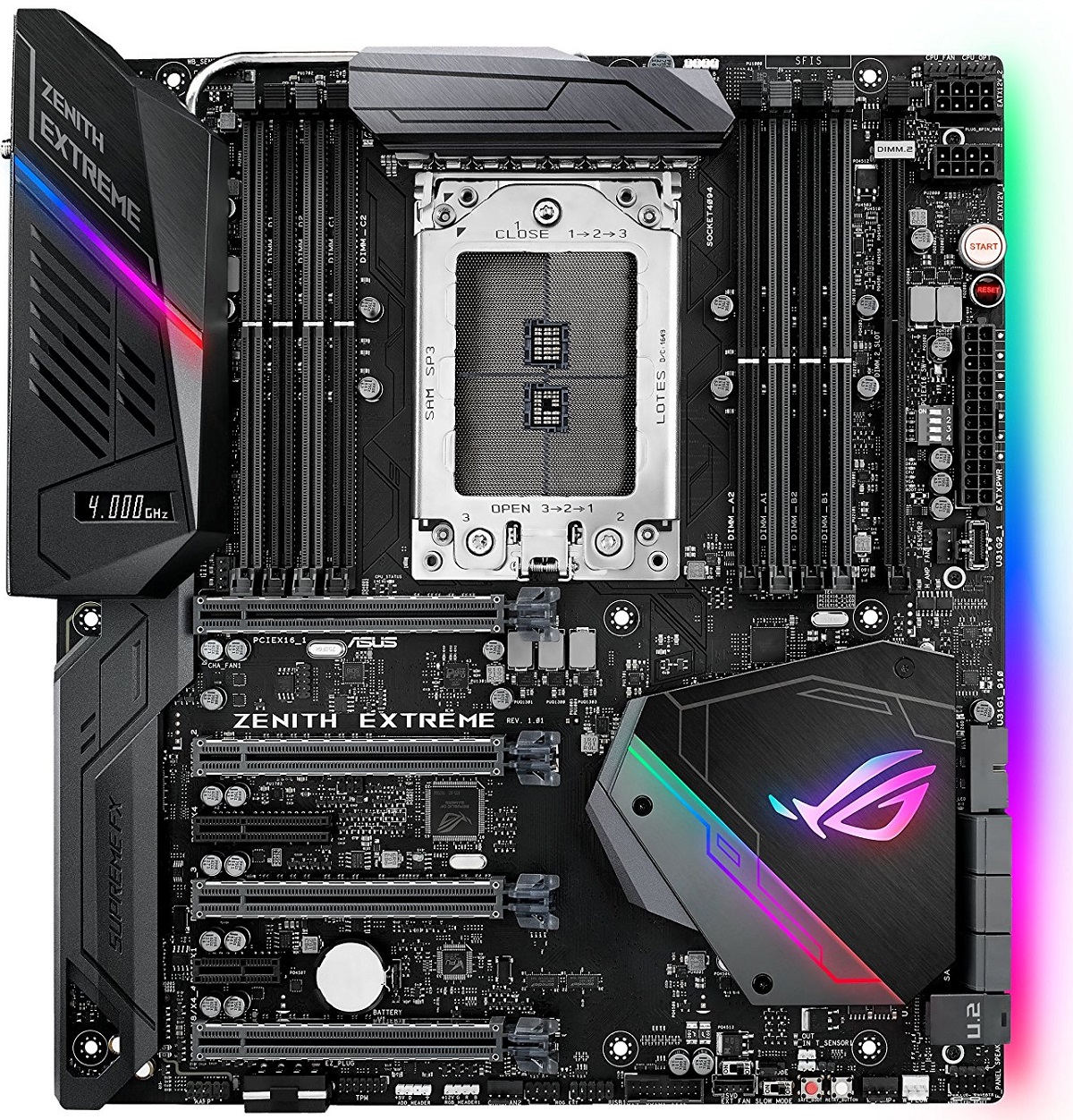

An E-ATX motherboard measures 12 x 10.9 inches or 30.5 x 27.7 CM in dimensions making it the biggest among the 4 form factors. The capability of an E-ATX motherboard is insane and they do not come into the budget category anyways. Their sockets and processors are different and are much more powerful.
Uses of E-ATX motherboards
The main advantage of an E-ATX motherboard over the other types of motherboards is that it comes with 8x DIMM slots. Similarly, other ports, slots, and connectors are more in quantity than on any other motherboard type. There is no defined limit and therefore, the cost also increases with features. These motherboards acquire a lot of space and require at least full-Tower cases which are really huge.
Features
E-ATX motherboards have a lot of PCI-Ex 16 slots, generally 4 or more than that, and 8x DIMM slots for RAM. An E-ATX motherboard can support 3-4 Graphics cards in SLI or CrossfireX easily depending upon the capability of a graphics card. RAM capacity is very high in these motherboards which is generally 128GB in the case of modern motherboards. Most of these have inbuilt wifi, sound cards, and onboard troubleshooting features and have very powerful VRM sections for stable overclocking.
Components Of A Modern Motherboard
A motherboard has several components. These perform particular operations. Have a look at what these are and what they do:-
CPU socket
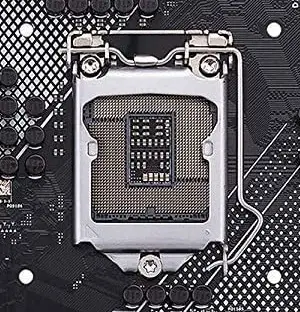
The computer’s brain or the Processor goes in the CPU socket. There are two major processor manufacturers right now: Intel and AMD, each of which produces processors for different sockets. They are not interchangeable and their sockets are different from each other.
A CPU socket comprises several hundred pins that get in direct contact with the processor chip or a socket may have several hundred pinholes as in the case of the latest AMD AM4 socket. Both Intel and AMD have released various sockets in the past decades that support a particular generation or generation of processors.
VRM
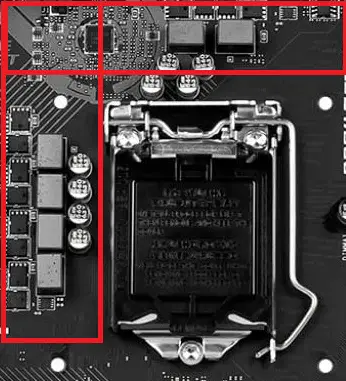
VRM stands for Voltage Regulator Module and it’s responsible for regulating the voltage from the power supply for the correct voltage to the CPU. A power supply has a +12VDC EPS power connector that is responsible for supplying the voltage to the VRM and the VRM converts the 12V into a voltage of somewhere between 1.1V to 1.4V which depends on various factors. A VRM consists of three components: Capacitors, Chokes, and MOSFETs which are there to ensure that the power supply is stable and controlled.
DIMM slots
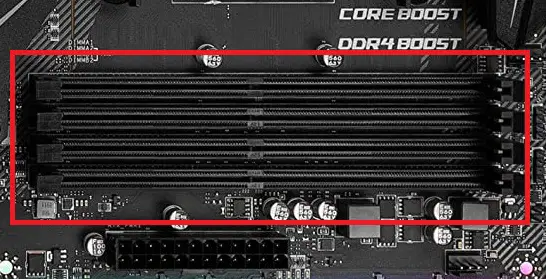
RAM sticks go in the DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) slots. These differ from storage drives as hard drives can store data permanently even after the power supply is cut off. DIMM slots quantity varies from board to board. A modern motherboard with any of the 4 form factors can consist of DIMM slots ranging from 2 to 8.
PCI or Expansion slots
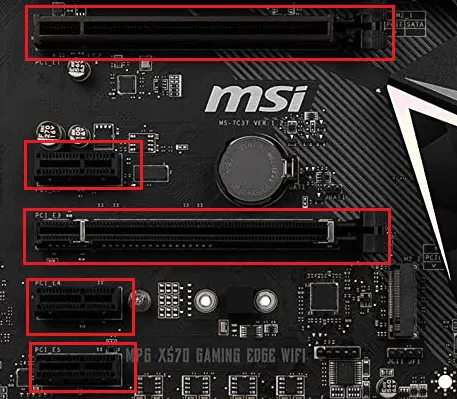
Expansion or PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) slots are for connecting peripherals directly to the board using PCI slots that differ in size and capability. The most common PCI slots today are PCI-E x1 and PCI-E x16. Older motherboards featured AGP slots for video cards that are. PCI-E x16 slots have replaced them in the newer motherboards.
SATA
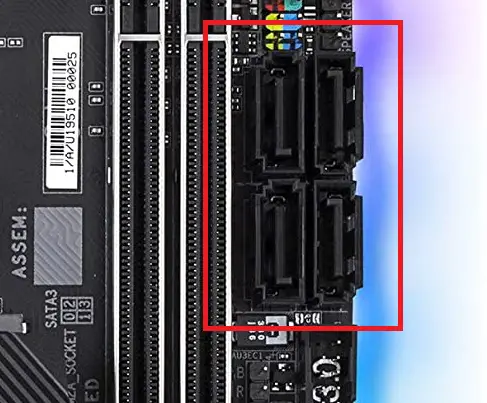
SATA which stands for Serial Advanced Technology Attachment is an interface that connects a storage device like a hard drive or a solid-state drive to the motherboard. Unlike the other components, a SATA cable with 7 pins connects SATA drives to the motherboard.
M.2
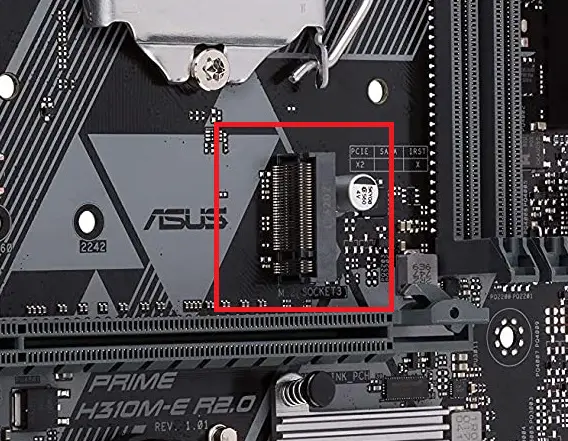
M.2 is amongst the latest additions to the motherboard. It serves as an interface to connect SSDs, Wifi, Bluetooth, etc. An NVME SSD connected through the M.2 connector doesn’t get bottlenecked unlike through the SATA port as it gets 4 PCI lanes to transfer data resulting in speeds that are several times faster than the SATA drives. Most of the Intel and AMD motherboards nowadays feature at least one M.2 slot.
Audio

Every motherboard has a dedicated Audio section near the audio jacks at the I/O. It can be identified by a PCB circuit line that has capacitors. High-end motherboards have more components in the audio section for crystal-clear sound.
CMOS battery
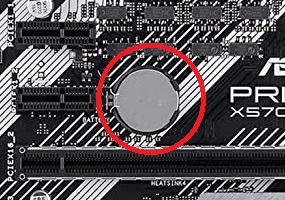
The CMOS battery is a Non-volatile RAM that is present in every motherboard and can be identified easily as it is silver and round in shape. This battery is responsible for storing the hardware information such as the specs of CPU, RAM, Disk Drives, graphics cards, etc. in the BIOS and is also responsible for the correct time and date.
Headers

Headers connect the peripherals to the motherboard. Components like chassis fans, CPU fans, front panel Audio and USB ports, RGB devices, etc. use these headers. Each of these headers has a different pin configuration and works on a particular voltage.
Power Connectors
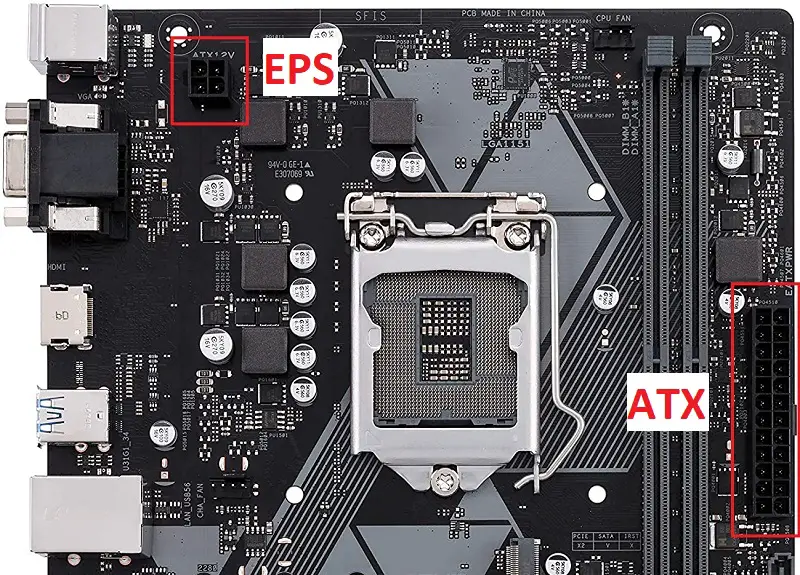
There are two connectors that power the motherboard and similarly, there are different power connectors for components. Some of the components don’t need additional power connectors on the motherboard such as RAM, Storage drives, and low-profile graphics cards which draw the power from the slots.
There are two main power connectors: ATX and EPS. Their pin configuration varies from board to board. While the ATX power connector powers the motherboard, the EPS power connector supplies the power to the VRM.
I/O

Every motherboard has an Input/Output section at the rear where several ports are present to connect the peripherals. Ports like USB, PS/2, HDMI, VGA, LAN, and Audio jacks are available here to connect the devices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which type of motherboard is best?
While each motherboard form factor is good at its place, an ATX motherboard is generally the best one as it provides more features, better compatibility, and easy upgradability over the Mini ITX and Micro ATX boards. E-ATX boards are also great but not a lot of cases are out there which can support them.
What does ATX mean?
ATX stands for Advanced Technology eXtended. It was designed by Intel in 1995 and is currently the most common form factor.
What are the main components of a motherboard?
While there are many important components on a motherboard, there are two components without which your computer won’t work at all. These are CPU sockets and DIMM slots. The CPU socket is for the processor and the DIMM slots hold the RAM sticks.
How do I find motherboard specs?
The best way to find the specs of your motherboard is to check its manufacturer’s official product page. Currently, all the manufacturers have a dedicated product page for their motherboards where you can find all the information related to their boards.