The quest for longer battery life on laptops and portable devices is an ongoing pursuit for both manufacturers and users. Undervolting, a practice often associated with desktop CPUs, has gained attention as a potential solution to extend battery life in laptops and mobile devices.
But does undervolting really make a significant difference in prolonging battery life or does it have no impact on it at all?
To understand this, we have to consider all the factors that go into undervolting and how they can affect the battery life of a mobile device.
Understanding Undervolting
While overvolting requires increasing the voltage supplied to the CPU, Undervolting involves reducing it to the CPU or other components while keeping their clock speeds unchanged. This practice is primarily aimed at reducing power consumption and heat generation while maintaining stable system performance.
The Role of Voltage in Power Consumption
Voltage plays a critical role in determining a CPU’s power consumption. In simple terms, higher voltage levels lead to increased power consumption. When a CPU operates at a lower voltage, it requires less electrical power, resulting in reduced energy consumption.
The Potential for Battery Life Extension

Undervolting has the potential to extend battery life in laptops and mobile devices, but the actual impact can vary depending on several factors:
- CPU Model: Not all CPUs are created equal. Some processors are inherently more power-efficient than others. Undervolting can have a more substantial impact on processors that are designed to operate efficiently at lower voltages.
- Usage Patterns: The extent to which undervolting extends battery life also depends on how you use your device. If your typical tasks are CPU-intensive, such as gaming or video editing, undervolting may yield more noticeable benefits compared to light web browsing or document editing.
- Thermal Constraints: In laptops, thermal constraints can limit the effectiveness of undervolting. If a laptop’s cooling system is already pushing its limits, undervolting might not result in a significant reduction in power consumption because the CPU’s power-saving mechanisms may not activate due to thermal throttling.
The Importance of Balance
While undervolting can reduce power consumption and extend battery life, it’s essential to strike a balance to avoid system instability. Overly aggressive undervolting can lead to system crashes and instability, negating any potential battery life gains.
The decision to undervolt or overclock your CPU depends on your specific needs and circumstances. If you require high performance and your laptop remains plugged in with efficient cooling, overclocking may be an option. However, most laptop CPUs are multiplier-locked, limiting the extent of overclocking. In such cases, you can maximize your laptop’s performance within its stock capabilities.
Conversely, if you prioritize power savings or wish to reduce CPU temperatures, undervolting is a viable solution. By limiting your CPU’s maximum multiplier, you can achieve lower power consumption and cooler operating temperatures. It’s essential to note that undervolting can potentially lead to system instability, but the risk of hardware damage is minimal. For Intel processors, tools like ThrottleStop can be used to adjust the multiplier and manage clock speeds effectively.
Practical Considerations
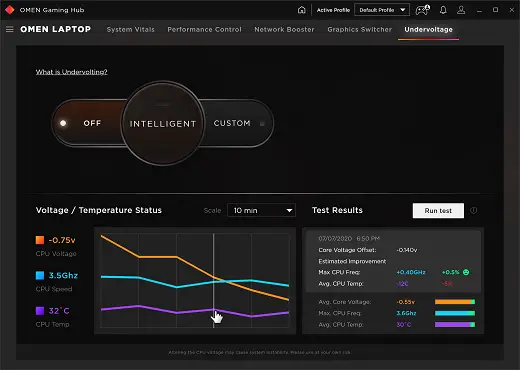
If you’re interested in undervolting your laptop or mobile device to increase battery life, here are some practical considerations:
- Use Proper Tools: Ensure that you use reliable and reputable software tools for undervolting. Many CPUs offer undervolting options through software utilities provided by the manufacturer.
- Test and Monitor: After undervolting, thoroughly test your device under various usage scenarios to ensure stability. Monitor system temperatures and performance to verify that undervolting does not lead to overheating or performance degradation.
- Start Conservatively: Begin with conservative undervolting settings and gradually fine-tune them. Avoid aggressive undervolting that could lead to instability.
- Keep an Eye on Cooling: Pay attention to your laptop’s cooling system. If undervolting allows the CPU to run cooler, the cooling system may be able to operate more efficiently, further contributing to power savings.
Final Words
Undervolting has the potential to increase battery life in laptops and mobile devices, primarily by reducing CPU power consumption. However, the actual impact varies based on the CPU model, usage patterns, and thermal constraints. To make the most of undervolting, it’s crucial to strike a balance between power savings and system stability while using proper tools and monitoring your device’s performance.
Undervolting alone may not provide a dramatic increase in battery life, but when combined with other power-saving practices, it can contribute to longer battery usage on portable devices.