TRIM is a critical feature in modern Solid State Drives (SSDs) that plays an essential role in data recovery as well as performance optimization. All storage devices that are Flash-based deal with previously deleted data in their own unique way, including SSDs.
In case a file has been deleted, whether it is in Windows or any other Operating System, the OS takes it that the original address is now empty and can be put to use again if need be.
TRIM comes in to avoid overworking the OS and slowing down the performance of the SSD. Let’s get to know in depth what TRIM is, how it works, and its significance in SSD data recovery.
What is TRIM?
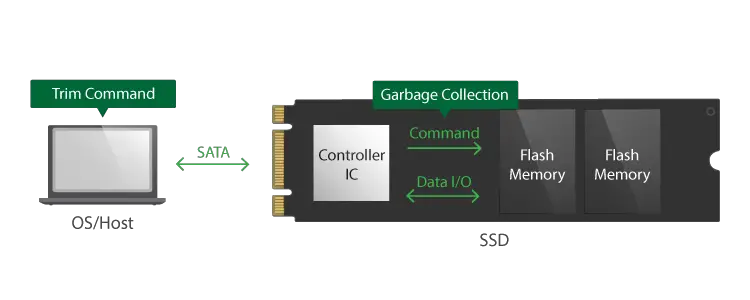
TRIM is an Advanced Technology Attachment (ATA) command which permits the Operating System to relay a message to a NAND flash SSD, that certain blocks of data are not in use any longer and it is safe to erase or wipe them. This information is critical because SSDs use flash memory, which has to be erased first before being written to, unlike the traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs).
If a block of flash memory has already been used prior, the process of writing new data to it is much slower. It is therefore essential to ensure the SSD’s performance is well maintained over time.
Performance Optimization with TRIM
SSDs that are NAND flash-based read and write data in units that are referred to as pages. In a typical SSD, a single data block contains 128 pages. When a file has been deleted from an SSD, the actual data still remains on the flash memory even though the Operating System marks it as free and available for future use.
In the absence of SSD TRIM, the performance of the SSD diminishes, since it gets to undergo extra work when it is being written on.
Before writing on an SSD, a whole block of data that is not in use has to be deleted. This process is referred to as Garbage Collection, and it results in decreased performance since it slows down the write speed.
Garbage collection manages the storage space available, keeping the disparity between the block and the page in check. These are the erase unit size and the read/write unit size respectively. When a block that was previously written becomes a target for garbage collection, the data pages that are still valid are gathered together and transferred to another block on the SSD.

Once this happens, the block with the invalid data pages can now be cleaned up.
When there is an efficient garbage collection process, the drive performs exceptionally well even several months down the line. However, if a drive does not have efficiency in garbage collection, it tends to slow down as time goes by. This is because the SSD’s controller has to work more and handle the recycling of all blocks that have garbage data.
TRIM ensures that discarded and invalid data is not copied when garbage collection takes place. It allows the SSD to be proactive in erasing the blocks that are marked as unused. This in turn helps in performance optimization. Whenever the Operating System sends a TRIM command, it becomes known to the SSD that the data in those blocks are safe to wipe off.
As a result, they immediately become ready for write operations. This entire process allows the SSD to maintain its initial performance levels while speedily performing write operations and managing to recover formatted SSD space more efficiently
[wpsm_top postid=”68324″]For TRIM to work, the Operating System and the SSD of the host have to support it. In a Windows environment for instance, when there is TRIM support reported by the SSD, the Operating System enables TRIM after it disables disk defragmentation.
When a file is deleted by a user, the Operating System sends a TRIM command to the SSD controller, telling it the data pages that can be deleted during garbage collection. It is also important to adhere to the conditions for the successful recovery of a formatted SSD because TRIM makes it rather difficult to use traditional recovery options.
Both the write command and the TRIM command operate independently. There is the option of initiating the TRIM command manually or scheduling it daily.
Benefits of Using TRIM
TRIM keeps your SSD in shape and ensures that its performance is good and speedy. If you do not use TRIM, it, therefore, implies that the performance of your SSD will slow down over time.
TRIM command reduces the chances of gathering invalid data during the garbage collection process. Once the amount to be moved is reduced, the erase cycles are reduced and the drive’s longevity is increased.
TRIM vs. Defragment
TRIM and defrag are two different things. TRIM is unique to SSDs. On the other hand, defrag refers to the rearrangement of data fragments that constitute a file into closer proximity on a hard drive in order to speed access. SSDs do not require traditional defragmentation because they do not have moving read/write heads. TRIM command ensures performance optimization by telling the Operating System the invalid data that it should ignore.
Data Recovery with TRIM
TRIM is beneficial in performance optimization, but it also poses a potential challenge with regard to data recovery. Execution of TRIM, as mentioned earlier, allows the SSD to erase blocks that are marked as unused. This makes it difficult to use traditional file recovery methods since the wiped data can no longer be accessed by the traditional SSD recovery software.
This means that TRIM significantly reduces the chances of recovering files that have been deleted from an SSD. You will need to use top-ranked SSD data recovery software for file restoration like Disk Drill by CleverFiles. In order to increase the chances of recovering data on an SSD, it is vital to stop using the drive at the very moment that data loss has been detected. Any write operations going forward may lead to overwriting the data that had been deleted.
Final Words
SSD TRIM, in summary, is a vital feature in SSDs that allow for efficient garbage collection, thereby leading to write speeds being faster. It basically optimizes and maintains the original performance of an SSD.
Its downside is that it comes with a data recovery challenge, as it can make deleted data become irretrievable. Users need to be wary of this fact even as they consider exploiting the benefits of TRIM, and be ready for regular backups that can help in safeguarding important data on SSDs.




